Induction heating
Induction heating
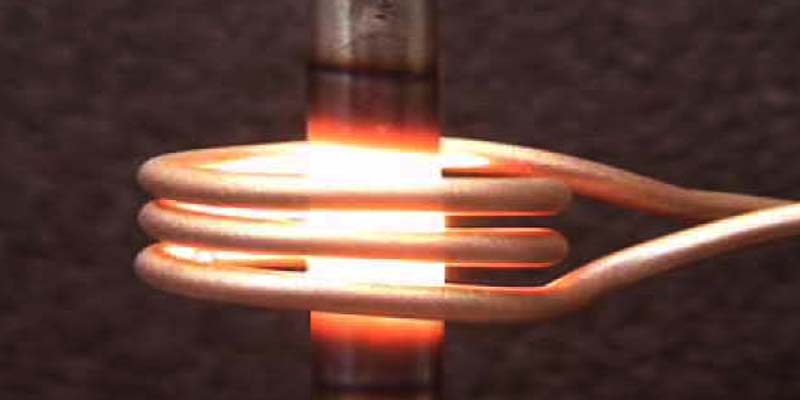
Induction heating is a well-established heating system that many still think about new technologies. Though induction technology is coming 100 decades of commercialization, misconceptions and questions surrounding its program still exist. As an instance, one common mistake is that the heating system is only going to heat magnetic parts. But, may be used to warm any electrically conductive material.
It’s also essential to think about both brazing and system as different and unique processes to comprehend and employ them. Brazing is a linking procedure, while is a heating process that’s frequently used as one measure of the brazing procedure.
A lot of studies and texts are published about brazing and other metal-joining practices. It’s not the aim of the paper to show all of the details connected with brazing procedures. Instead, general rules of thumb will be introduced to get a comprehensive discussion on heating technologies. This article also addresses common misconceptions of the system regarding its brazing-related applications.
heating is a corrective procedure where electrically conductive material is placed inside a varying magnetic field and warmed through hysteresis (magnetic substances only) and triggered electric current (all conductive elements). a heating system is a non-contact heating system that’s extremely fast and effective compared to other heating technology used for brazing.
There’s one crucial distinction associated when warming a magnetic component vs. a nonmagnetic part. Magnetic elements, for example, iron, have magnetic contaminants inside their atomic arrangement known as domain names. All these domains are like little bar magnets. Since the magnetic field reverses, the areas change direction. This constant shifting of management leads to internal friction heating. This heating via magnetic domain is referred to as hysteresis heating system. Hysteresis only happens in magnetic substances and also is the most effective kind of heating system. Additionally, it may exceed 90% efficacy.
When adequately heated, magnetic substances will lose their magnetism. This is known as the Curie point (generally around 1400°F for iron). After a magnetic component reaches its Curie point, hysteresis warming stops. Without appropriate frequency and electricity choice, the heating tends to stall at roughly 1400°F. That is one reason some novices think heating won’t heat over 1400°F. With the appropriate frequency and power choice, it’s likely to heat to some temperatures up to a few thousand levels.
The higher the frequency of performance (Hz), The thickness where the present interrupts the Surface is known as the reference thickness and signifies the depth where 63 percent of Based on magnetic permeability and substance Resistivity, the reference thickness of heating may vary between 0.01 and 0.20
Induction heating,Induction heating,Induction heating,Induction heating,Induction heating,Induction heating


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!